Technology has advanced progressively over the last couple of decades, with giant leaps in technological capabilities with the introduction and development of artificial intelligence. In the following feature, we’ll take a look at what natural language processing is and how it has evolved to become an essential part of the software you use every day.
What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?

NLP is a strand of artificial intelligence known otherwise as computational linguistics. This type of programming allows computer systems to understand input from humans and utilise this information to engage in human-like conversation with users. NLP has cemented its value within business communications from bots to voice-activated platforms such as IVRs as we outlined in a previous blog. NLP, itself, has come on leaps and bounds since its integration into technology just a few decades ago.
The Evolution of Natural Language Processing
From humble beginnings, originating as thoughts in some of the smartest people in human history, to now being an integral part of human-to-machine interaction, natural language processing has been on a long journey. However, it is only in the last 40 years that NLP has accelerated in its capabilities to create smooth communication between humans and computers with the introduction of algorithms. In our timeline infographic, we pinpoint some of the key events and people that have progressed NLP and contemplate what the future will look like for technological adoption, including chatbot software.
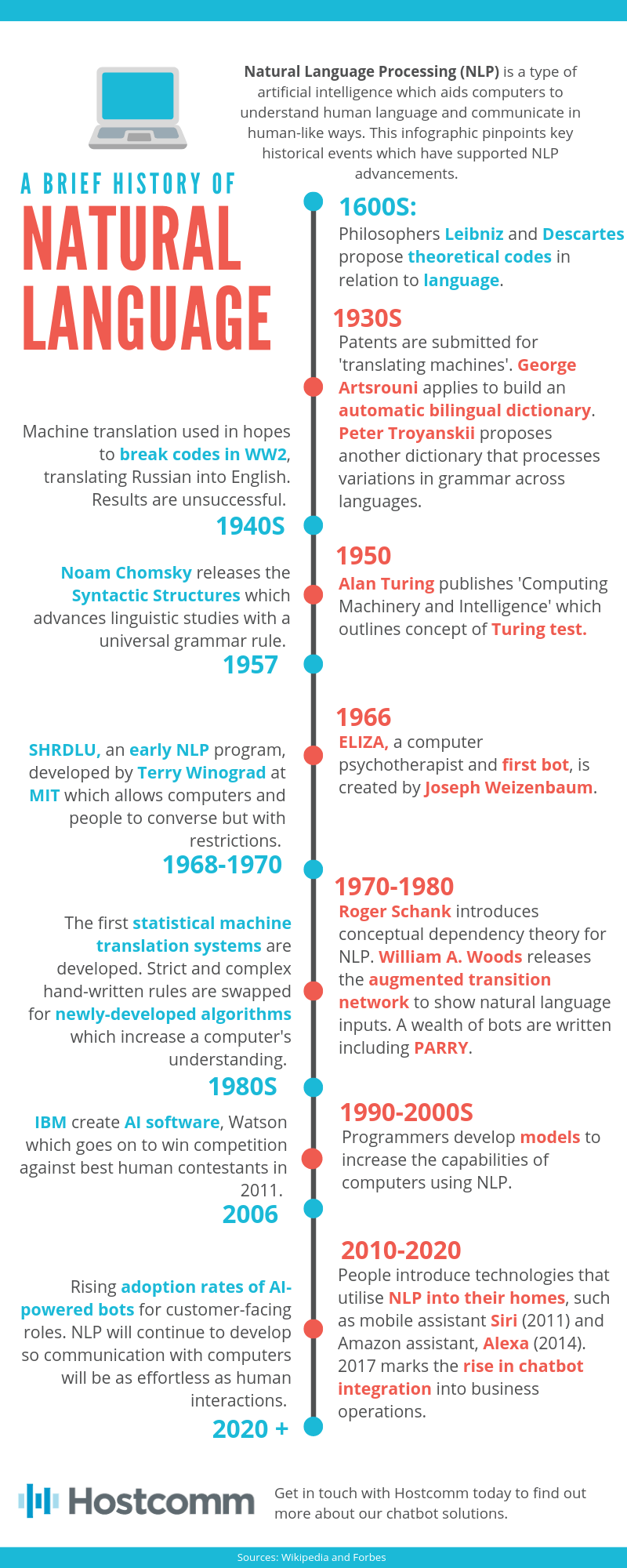
Below we delve into the history of natural language processing a little further to examine the events that led up to NLP’s application into bots.
The 1600s:
The roots of natural language processing began in the seventeenth century with philosophers Leibniz and Descartes. German-born Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was a key figure in multiple fields, contributing to philosophy, biology and physics as well as technology and linguistics. Similarly, René Descartes was a man of many talents who offered insights into philosophy, mathematics and science. Along with their contemporaries, they proposed codes concerning language and communication. Of course, the proposals remained theoretical as technology was not yet in a position to realise their visions into a machine. However, it is their thoughts that provided the foundation for natural language processing.
The 1930s:
Over three centuries pass before patents for ‘translating machines’ are submitted. Proposal masterminds such as Georges Artsrouni and Peter Troyanskii offer detailed looks into how an automatic bilingual dictionary would operate. Both were forming the basis of systems that could translate one language into another. Bilingual dictionaries were the catalyst for the development of machine translation (MT) which provided a platform for the creation of NLP.
The 1940s:
Bilingual dictionaries were particularly attractive to militaries from the beginning of the second world war. Early MT efforts were utilised to break codes during the war, with developers hoping their systems could translate Russian communications into English. Despite the failure in decoding, it was this application of MT that paved the way for more sophisticated technologies to come.
The 1950s:
Alan Mathison Turing, an English mathematician and computer scientist, was a crucial individual in the development of the theoretical computer science we utilise today. His contribution to computer science is so significant that he has been nicknamed the father of computer science and artificial intelligence. In 1950, he published an article called “Computing Machinery and Intelligence” which now forms the basis of the Turing test. The Turing test is a criterion of intelligence in computing systems based upon the system’s ability to impersonate human communication.
The 50s was also the era of another significant step in computational linguistics with Noam Chomsky’s Syntactic Structures. It was this that introduced a universal grammar rule for syntax which provided the basis of rules that computer systems could be programmed to follow.
The 1960s:
The 60s provided us with some of the first successful applications of NLP. One such example is SHRDLU, which was developed at MIT by Terry Winograd between the years 1968 and 1970. The system was smart by allowing users to communicate with computers; however, it suffered from several restrictions. While it wasn’t anything like we use today, it was a stepping stone in the right direction.
Beforehand, the first bot was created in 1966. The system was called ELIZA, and it undertook the role of a psychotherapist. It could converse by using the information provided by users and offered responses based upon a programmed script.
The 1970s:
Roger Schank introduces the conceptual dependency theory for natural language understanding utilised in AI systems. The model was developed at Stanford University, but many of Schank’s students at Yale realised its potential for their work. The model’s aimed to represent the knowledge gained from input. It has been used in many systems since its conception.
Around the same time in 1970, William A. Woods introduces the ATN (augmented transition network) which represents the input. Moving away from phrase structural rules, the ATN would translate real-world information into data the computer would understand. This was applied to many of the technology of the time, including chatbots such as PARRY.
The 1980s:
Previously, systems that used NLP did so by following a set of hand-written rules. Developments from the era previous paved the way for NLP to develop. It was in the late 80s that machine learning was introduced that utilised algorithms to understand human input. Increases in computational power allow for such developments to be implemented in computers, governed by Moore’s Law.
The 1990s:
Developers continue to build on the success of machine learning systems. They work to create models that increase the capabilities of computers and improve human-computer communication. IBM leads the way with research.
The 2000s:
IBM created Watson in 2006. This AI software is designed to answer questions. It was so good that it goes on to win a contest of Jeopardy! against the best human players in 2011.
The 2010s:
Software supported by NLP integrates into systems used in homes such as Siri (2011) and Alexa (2014). The benefits of these technologies are realised by businesses who begin to adopt bots from 2017 onwards.
2020 and beyond:
More and more businesses will adopt bots into their operations. As the technology develops, many experts believe they will take on more customer-facing roles that take customers from discovery to purchase to aftercare. Natural language processing will continue to advance as programmers trial and test their developments to make communication with computers as effortless as human interactions.
To learn more about the role of NLP in our chatbot solutions, get in touch with us today. We are more than happy to discuss how our bots can work within your business and the benefits you can realise from its integration. We have been in operation for more than fifteen years, helping small businesses just like yours.
Discover our chatbot solution here: http://www.hostcomm.co.uk/solu...














